Lecture 5 Convolutional Neural Networks
Dl.cs231n.lecture| 27 Sep 2018
Tags:
DeepLearning
CS231n
- Convolutional Network: NN using convolutional layers
- We want to preserve spatial structure of image! But Fully connected NN cannot do that.
- preserve (horizon * vertical * channel) structure
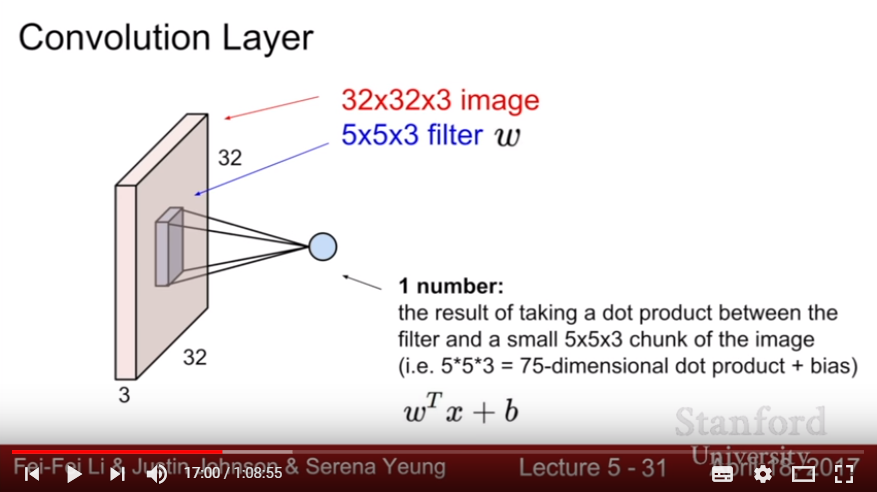
- For 32 * 32 * 3 image,
- convolve the filter(5 * 5 * 3)(or receptive field for each neuron) with the image spatially
- elementwise multiplication(dot product), which results in one value
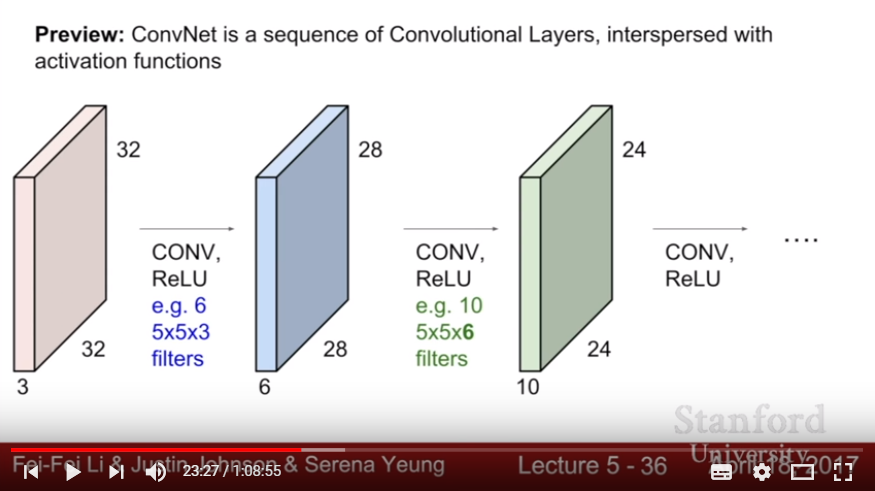
- with 6 filters, activation map becomes (28 * 28 * 6)
- Stride is assumed to 1. If assume stride = 3, then the size of activation map becomes (10 * 10 * 6).
- That is, (32 - 5)/3 + 1 = 10.
- If stride =2, then (32 -5)/2 + 1 = 14.5 :( ({size of image} - {size of filter})/{stride num} + 1 must be integer!
- In practice, we tend make zero pad border to make the size of activation map same with image size(when filter size is 3 * 3, zero pad might be 1 pixel. when filter size is 5 * 5, then zero pad might be 2 pixel)
- Stride is assumed to 1. If assume stride = 3, then the size of activation map becomes (10 * 10 * 6).
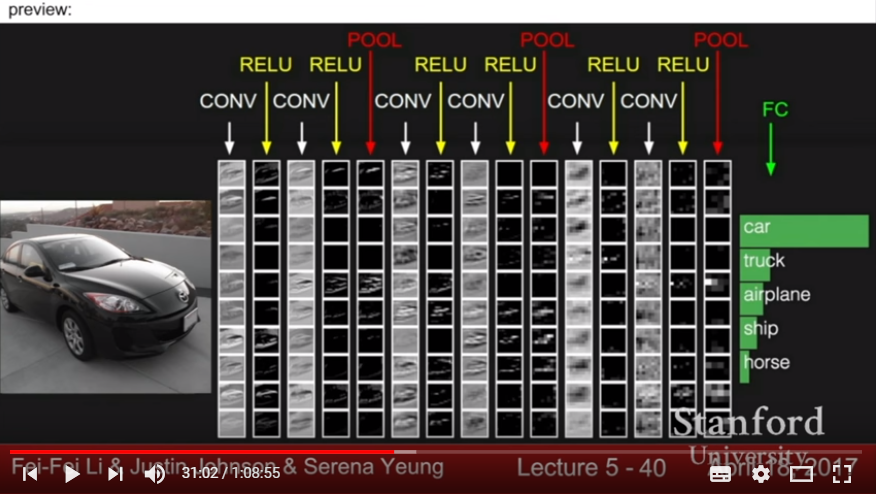
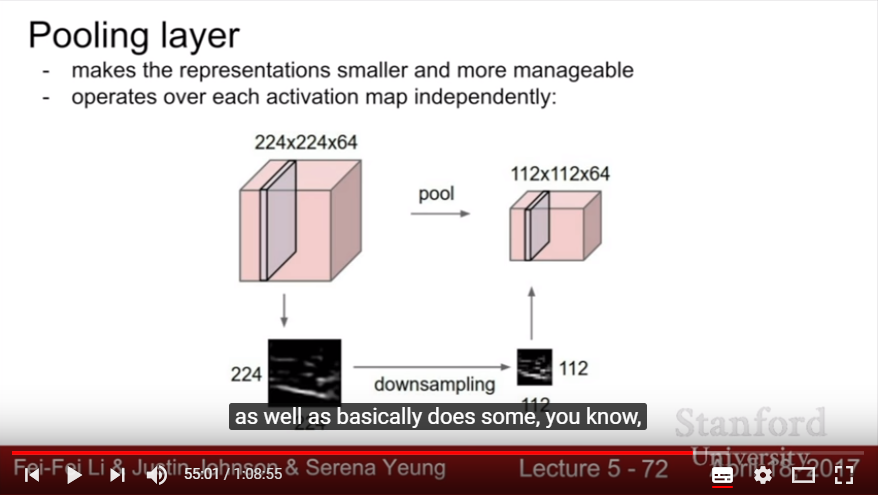
- include pooling layer(downsampling), which makes representations much smaller to manageable scale
- Max pooling or Average pooling
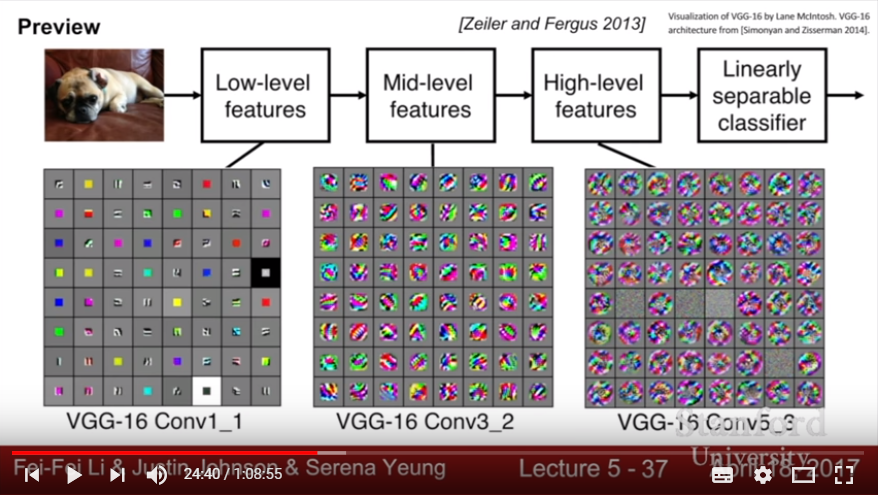
- looking at a local region- spatially! (unlike FCNN- take features from linear vectorization and dot product)



(Omit the history of CNN and range of image recognition & reconstruction)
